In this post I will be sharing notes on configuring a cisco device for use. By default, there is no authentication on line console 0. If you have received used gear you may have to do password recovery. Once all that is settled. The first step is to connect to the device using a console cable.
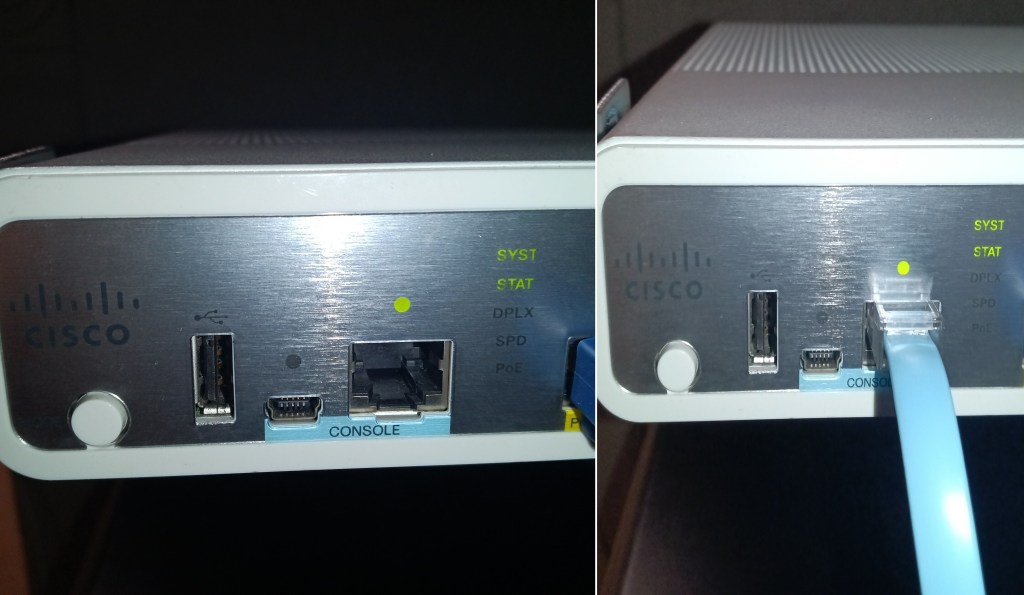

You may need to buy a serial-to-usb adapter. USB console cables can be purchased from a plethora of online retailer. Depending on your pc you will need to find which COM port your device is connected to.
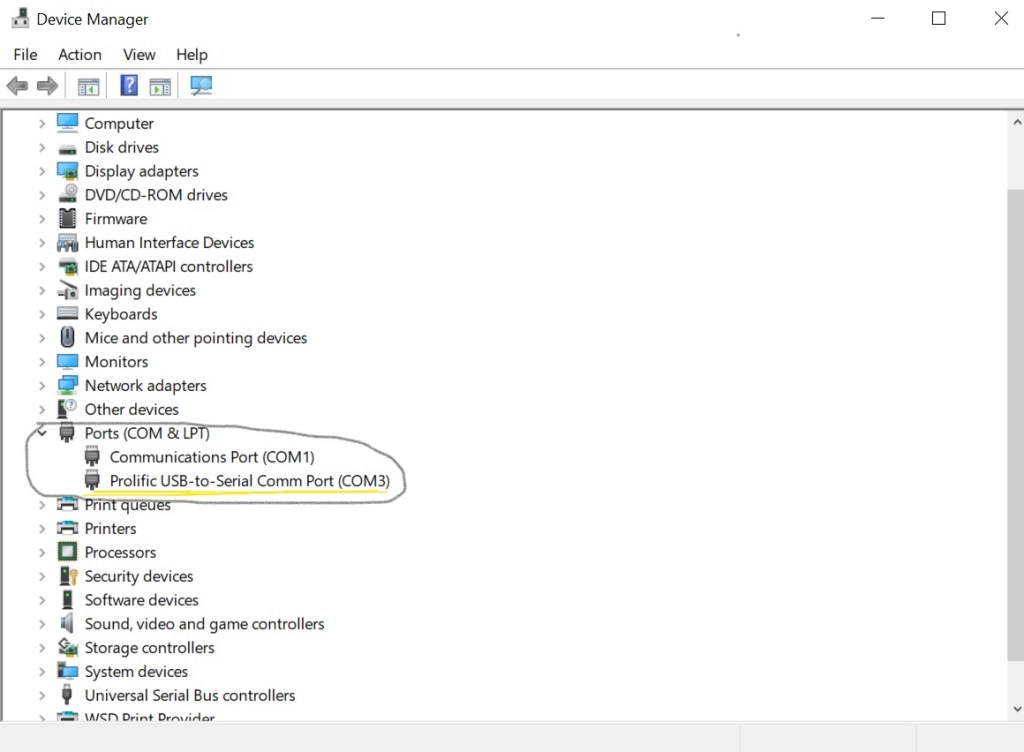

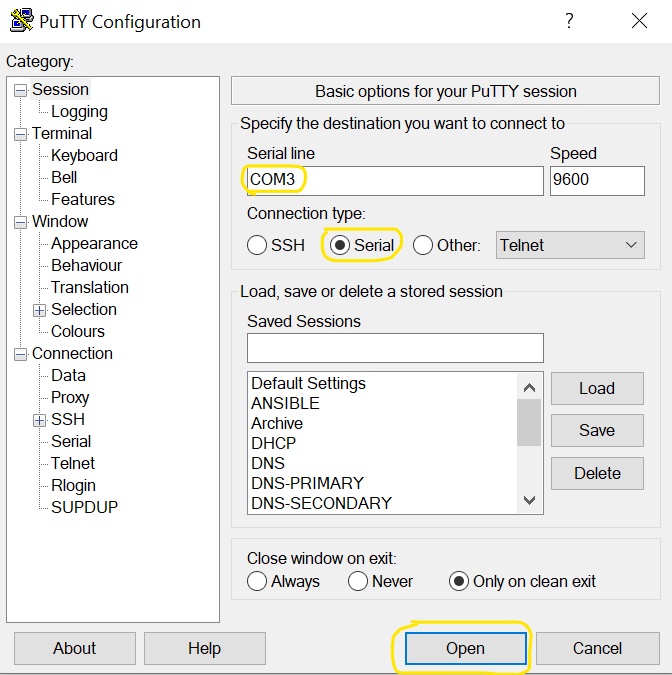
Once we are connected, we will be met with a screen.


Now we can begin configuration. You can choose whichever hostname you want to give the device as well as username. Here is a example configuration.
Router> Enable
Router# configuration terminal
Router(config)# hostname < choose a name>
<chosen name>(config)#ip domain-name <choose a name>
<chosen name>(config)#no ip domain-lookup
We will configure encrypted passwords, as well as ssh. The short is if someone is eavesdropping on our traffic. We don’t want them to get out passwords.
<chosen name>(config)#username < chosen username> algorithm-type <scrypt or sha256> secret < desired password>
<chosen name>(config)#crypto key generate rsa modulus 2048
Hit enter unless you want to designate different options.
<chosen name>(config)#line con 0
<chosen name>(config-line)#login local
<chosen name>(config-line)#exec-timeout 30 0
<chosen name>(config-line)#logging synchronous
<chosen name>(config-line)#transport output ssh
<chosen name>(config-line)#exit
<chosen name>(config)#line vty 0 4
<chosen name>(config-line)#login local
<chosen name>(config-line)#transport input ssh
<chosen name>(config-line)#transport output ssh
<chosen name>(config-line)#exit
<chosen name>(config)#enable secret <enable password here>
The enable password will be used to gain access to the device. It is independent of the username password. Without the enable password you will not be able to login through the vty lines.
<chosen name>(config)#interface loopback 0
<chosen name>(config-if)#ip add 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
Loopback interfaces are automatically brought up
<chosen name>(config-if)# exit
<chosen name>(config)#end
<chosen name>#write memory
Building configuration…
[OK]
<chosen name># show running-config
This command will show the current running configuration.
<chosen name># show startup-config
This command will show the startup-config. It will verify if our config saved.
Now to login to our device. The first prompt for a password, type in your username password. The second prompt for a password, type in your enable password.
<chosen name>#ssh -l <chosen username> 1.1.1.1
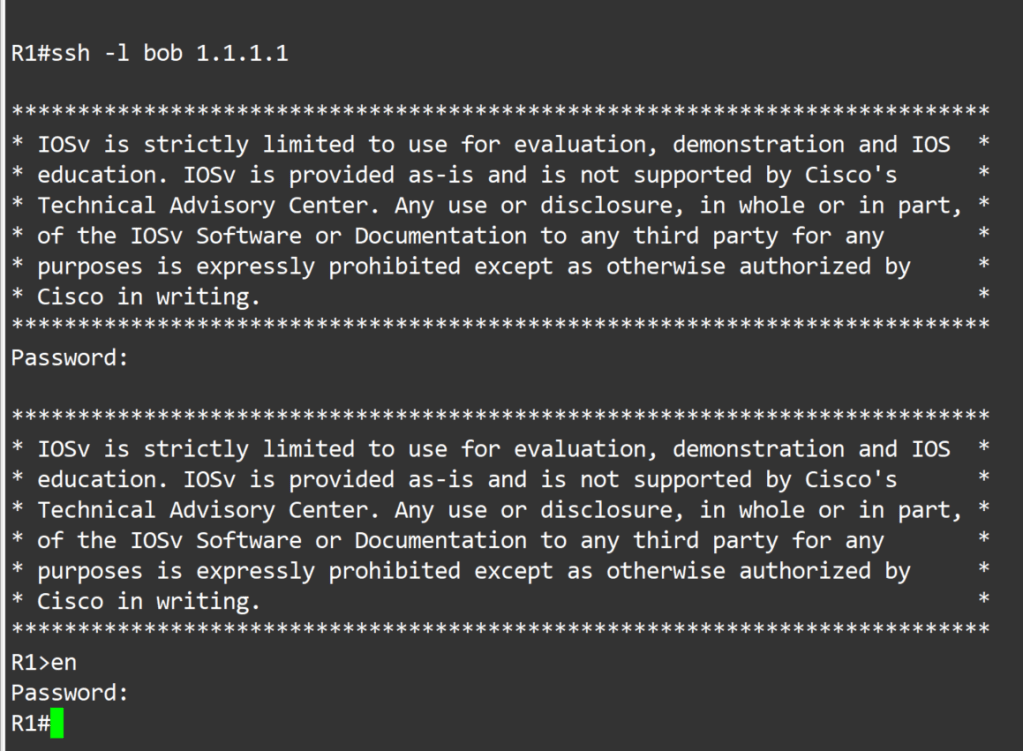
<chosen name># show users

-Notes
- Password Types
- 0 = unencrypted passwords ex- enable password < >
- 5 = MD5 algorithm preferred over 7 ex- enable secret
- 7 = Cisco Vigener cipher (weak) ex- service password-encryption
- 8 = Password-Based Key Derivation Function 2-PBKDF2 SHA256 consider uncrackable ex- username < > algorithm-type sha256
- 9 = Scrypt algrotithm ex- username < > algrotithm-type scrypt
- Transport preferred – protocol that will be used when typing ip address in usermode ex – <chosen name>#1.1.1.1
- Line con 0 transport output – protocol allowed from console ex-

4. You can change the source address for transport protocols with:


Router(config)#ip ssh source-interface <interface with configured ip address you want to use>
Router(config)#ip telnet source-interface <interface with configured ip address you want to use>
Thank you for your time.