- Authentication: Enables a user to be identified and verified prior to being granted access to a network devic and/or network services.
- Authorization: Defines the access privileges and restrictions to be enforced for an authenticated user.
- Accounting: Provides the ability to track and log user access, including user identities, start and stop times, and executed commands.
Tacacs+ – uses TCP port 49, open standard created by Cisco. It is mainly used for device access control. We will be installing it on Cent OS 7 and utilizing the service with a Cisco router.
Link to Cent OS official download site: https://www.centos.org/download/
Once you have your Cent OS 7 system up and running we will begin by downloading the Tac_plus application. Once at the terminal window we will enter:
cd /etc/yum.repos.d/

sudo vim tacacs-plus.repo

Press i to begin editing document.
:wq enter after you enter in this text:
[tacacs-plus]
name=Tacacs Plus
baseurl=http://li.nux.ro/download/nux/misc/el6/x86_64/
enabled=0
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=http://li.nux.ro/download/nux/RPM-GPG-KEY-nux.ro
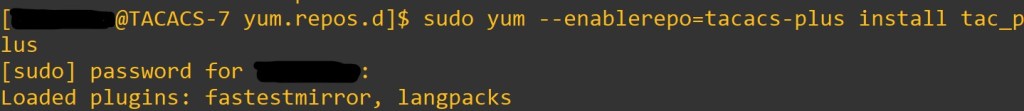
Next enter: sudo yum –enablerepo=tacacs-plus install tac_plus
When you copy and past it can mess up the — . I have experienced a few times.
Awesome, now we need to generate a password for our conf file.
Enter: tac_pwd
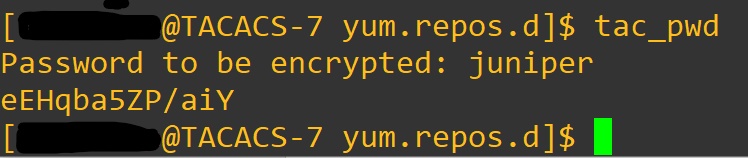
That will be pasted in the tac_plus.conf file. We open with:
Sudo vi /etc/tac_plus.conf


#key = “ something “ change to
Key = “ Key ” Enter in the shared key for client devices
acl = default { permit = 0\.0\.0\.0 <– enter the address that the device will use as source in packets sent to server.
} This is where the IP addresses of the client devices go.
Client Device = Routers, Switches, devices that will be contacting the server to authenticate users.
You can add new groups and users. Here is a example:
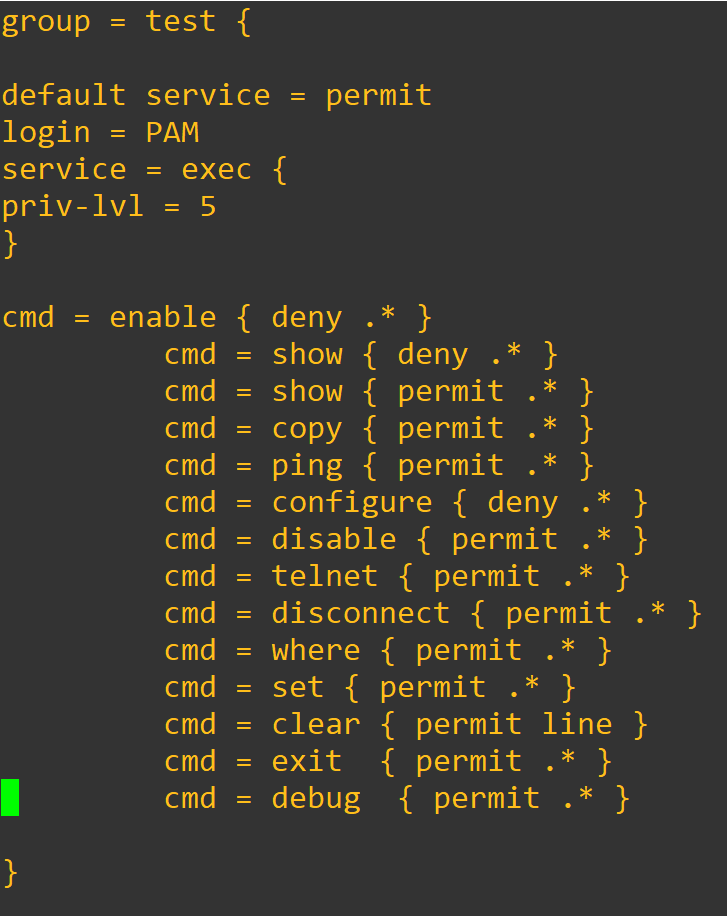
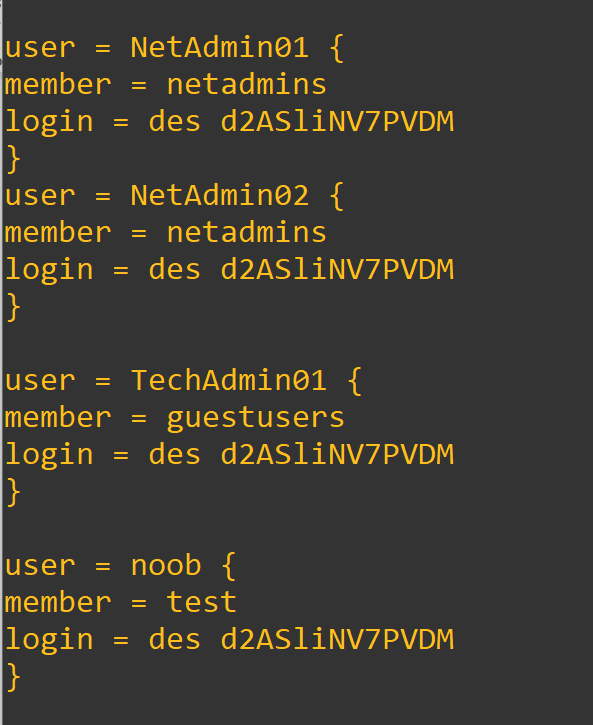
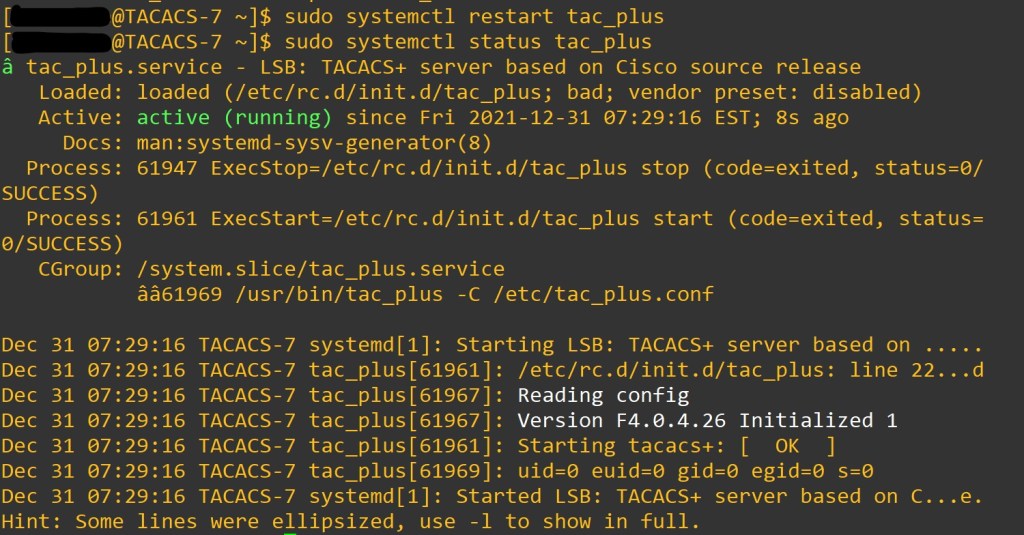
When we make changes to the program we want to restart the service.
sudo systemctl restart tac_pluc
sudo systemctl status tac_plus
Let’s not forget to add the firewall rules.
sudo yum install firewalld -y
sudo systemctl status iptables
sudo systemctl stop iptables
sudo systemctl mask iptables
sudo firewall-cmd –get-zones
sudo firewall-cmd –get-default-zone
sudo firewall-cmd –list-all-zones
sudo firewall-cmd –set-default-zone=internal
sudo firewall-cmd –get-default-zone
sudo firewall-cmd –get-zone-of-interface=eth0 <– Put your interface here, enter < ip a > at terminal
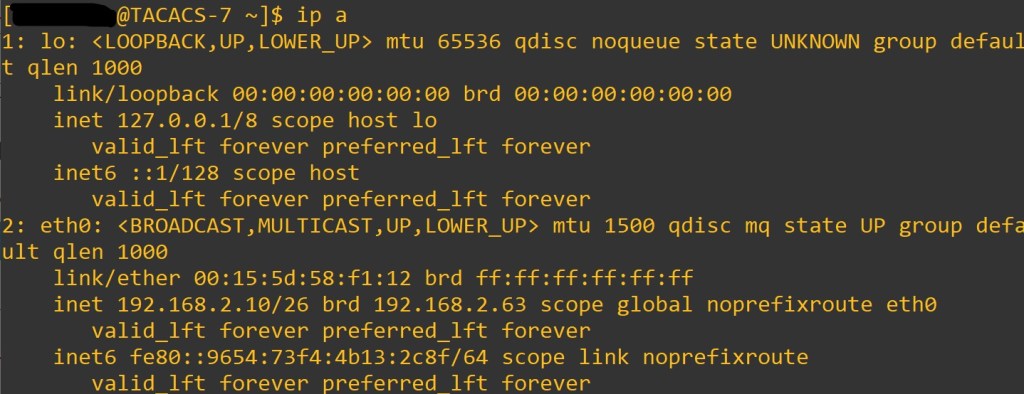
sudo firewall-cmd –get-icmptypes
sudo firewall-cmd –get-services
cd /usr/lib/firewalld/services/
ls <– to view services available
cd /etc/firewalld/services/
sudo cp /usr/lib/firewalld/services/ssh.xml /etc/firewalld/services/tac_plus.xmlcd /etc/firewalld/services/tac_plus.xml ^– used to copy ssh.xml to tac_plus.xml
sudo vi /etc/firewalld/services/tac_plus.xml <– edit service xml

sudo firewall-cmd –reload
sudo firewall-cmd –state
firewall-cmd –get-active-zones
firewall-cmd –get-service
Once we verify the port is open, we will configure our device to connect.
The commands:
Router(config)#aaa new-model
– enables aaa on device. By default, lines will use login local until a default method list is defined or a user defined method list is applied to the lines. Best practice to make a user account before issuing this command. To lessen the likely hood of locking yourself out of device.
- aaa new-model check list:
- enable secret <string>
- username algorithm-type < sha254 or scrypt> secret <string> <– may not be supported depending on your IOS version
- username < username> secret <string>
- crypto key generate rsa <– we want a key size of 1024 or above , then enter to defaults
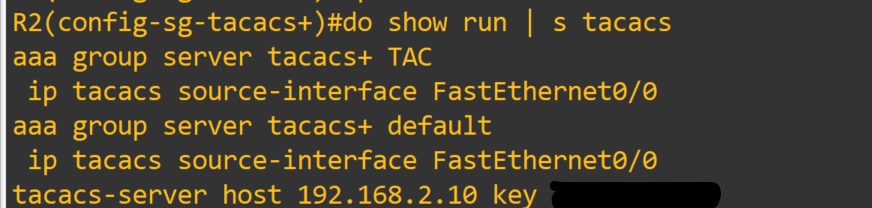
Router(config)#tacacs-server 192.168.2.10 key <Key> <- Shared key
- The servers need to be defined before being added to a group.
- Theses are by default part of the Tacacs+ group of servers after being defined.
Router(config) aaa group server tacacs+ <TAC>
Router(config-sg-tacacs+)#server 192.168.2.10
Router(config-sg-tacacs+)#exit
Router(config)#aaa authentication login default group <TAC> Local
- Default is the method list that will be called upon when the service needs to know which database to match against.
- TAC is the user defined group that will be used first for authentication. Local is the local database on the device that will be used second if the first method cannot be contacted.
Since we used the default method list the lines should be good to go. To view what is happening lets enter in some debug commands.
Router#debug aaa authentication
Router#debug aaa authorization Let’s try: I will use telnet to myself.
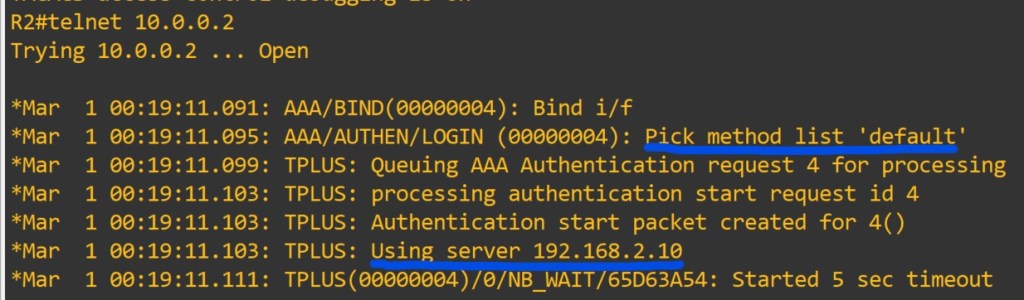
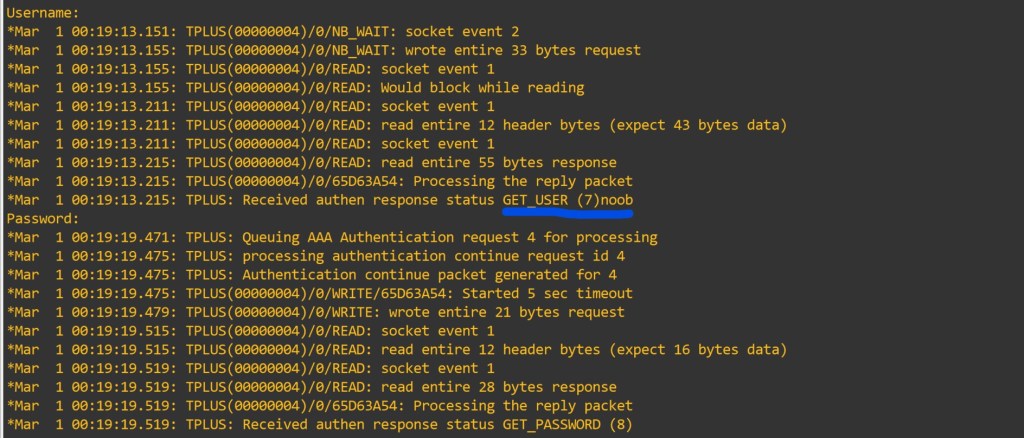

This user shouldn’t be privilege lvl 15. It shows we didn’t define a method list for authorization.
- AAA authorization exec enables EXEC shell authorization for all lines except the console line.
- AAA authorization console – Authorization for the console is disabled by default to prevent inexperienced users from locking themselves out.
- Privilege level 0 – includes disable, enable, exit, help and logout.
- Privilege level 1 – also known as User Exec mode. No configuration changes.
- Privilege level 15: Privileged EXEC mode. Highest privilege level.
- Privilege level 2-14 – can be configured to provide customized access control. ( either local or on server)
- When all the AAA servers are unreachable AAA command authorization might still be trying to reach the servers. This will prevent users from being able to execute any more commands. Safety measure use the if-authenticated method. Allows all commands to be authorized as long as the user has successfully authenticated locally.
Router(config)#aaa authorization exec default group tacacs+ if-authenticated
After entering that command, let’s test the functionality.

Since we defined allowed commands and privilege level to the group. Added the user to the group (on the server). We have restricted the users commands on the device from the server. We can also enable accounting very easily too.
Router(config)#aaa accounting exec default Tacacs+
Router(config)#aaa accounting commands 15 default start-stop group tacacs+
The log file location is in the tac_plus.conf file at the very top.

You have to define the privilege level you will be accounting.
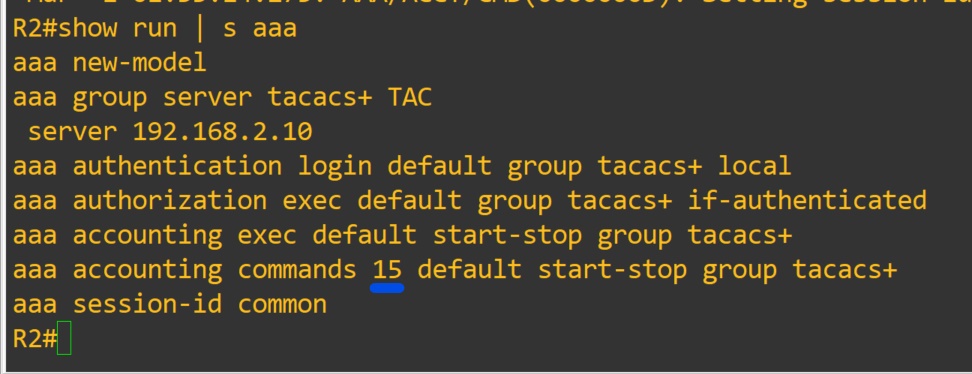
Show commands:
show run | section username|aaa|line|tacacs
-NOTES
- Do not allow the global enable password to be compromised. It will grant lvl 15 to users. Enable passwords for lower levels can be designated. Replace 15 with desired level. In a different post we will configure enable passwords of different levels. To utilize the enable passoword on the server. you would configure aaa authentication enable default group tacacs+

- Troubleshooting Notes:
- Check that server ip address is defined correctly on device.
- Check that the secret matches on server and device
- Check that you can connect to device via tcp port 49
c.1. You may have to install telnet
c.2. Telnet only works on tcp

- Sudo systemctl status tac_plus -l
Sudo journalctl -xe
- aaa authorization config-commands is enabled with aaa authorization exec command
- aaa authorization commands <priv level> { default | user defined list} – authorized all commands with the AAA server before executing them. Applied on a per-privilege level basis. A command authorization method list must be defined for every privilege level that requires command authorization.
- If the aaa authorization commands level method command is enabled, all commands, including configuration commands, are authorized by authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) using the method specified. Because there are configuration commands that are identical to some EXEC-level commands, there can be some confusion in the authorization process. Using the no aaa authorization config-commands command stops the network access server from attempting configuration command authorization.
- Examples
The following example specifies that TACACS+ authorization is run for level 15 commands and that AAA authorization of configuration commands is disabled:
aaa new-model
aaa authorization command 15 group tacacs+ none
no aaa authorization config-commands
- If the aaa new-model command has been configured to enable the AAA access control model, the no aaa authorization console command is the default, and the authorization that is configured on the console line will always succeed. If you do not want the default, you need to configure the aaa authorization console command.
User defined method lists must be applied to the lines to be used by device. We used the default list in this lab. Verify the line is configured with sh run | s line

Links to sources:
Install Configure Tacacs+ CentOS 7 RHEL 7 | Tech Space KH
How to Set Up a Firewall with FirewallD on CentOS 7 | Linuxize